Please download IntroExcel-Part1-SampleWorkbook.xlsx to follow along with workshop activities.
Throughout this workshop Click refers to a Left Click with your mouse
Introduction
In this introductory section, we will discuss key terminology and naming files.
Key terminology
An entire Excel file is called a workbook and every workbook includes one or more sheets.
When you open a new Excel file, Sheet1 is automatically created at the bottom of the workbook.
The data in Excel workbooks are organized into columns and rows.
The intersection between a column and a row is a cell.
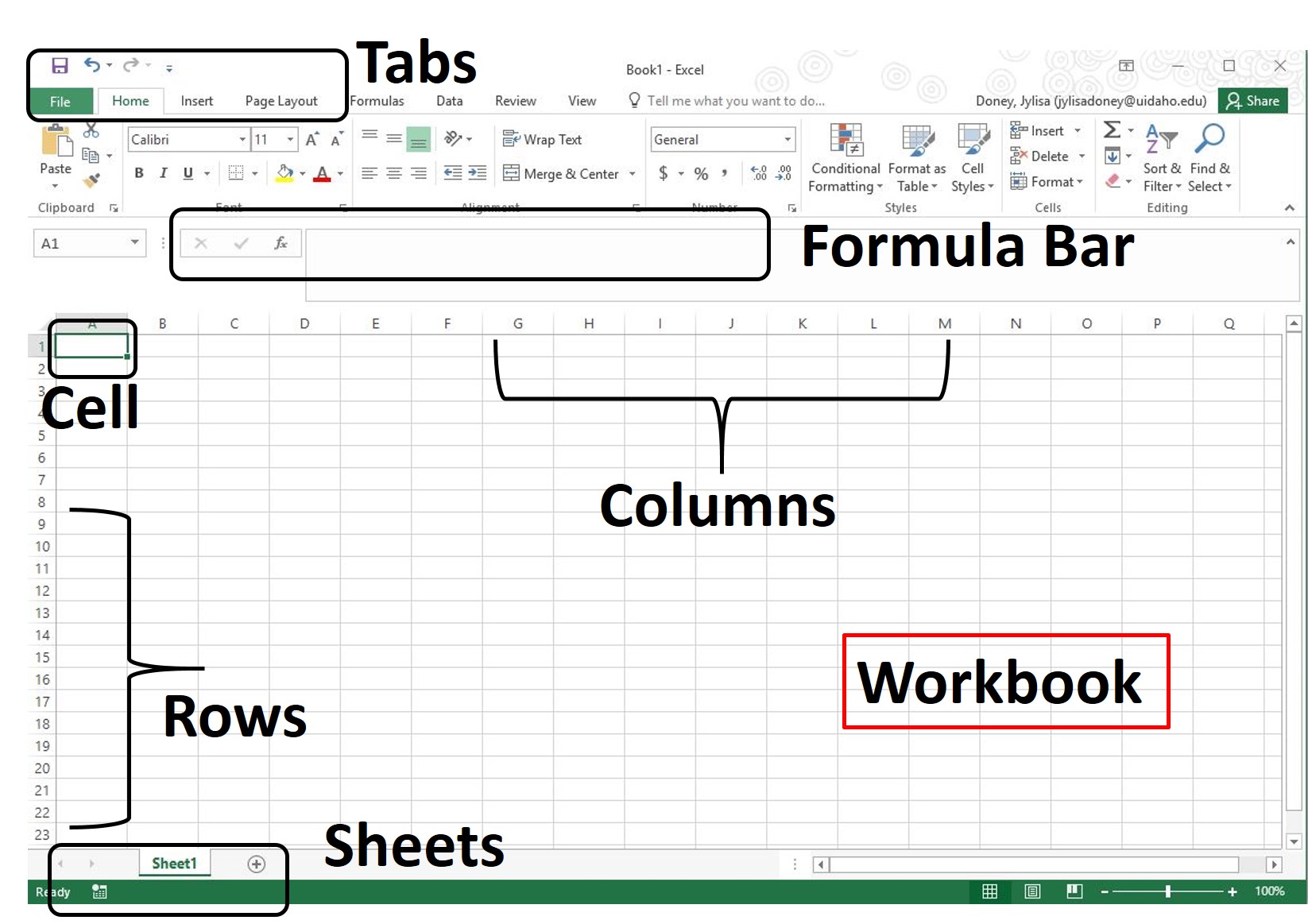
Tabs appear at the top of the workbook and help you utilize many Excel features, such as creating charts and graphs or sorting your data.
The formula bar is where you can see the formulas and functions you’ve inserted into certain cells.
Naming Files
It is important to save, name, and version an Excel workbook so it is easy to find in the future.
File names
In your file names, consider including:
- Assignment or project names
- Your name or initials
- Date of last edit
- Version numbers
- Geographic coordinates
- Type of data, etc.
For example: SOC320_SMM_20180205_v001
Characters
Spaces don’t work well in file names, but you can use underscores (_) or dashes (-) instead.
Special characters should also be avoided: ~ ! @ # $ % ^ & * ( ) ; < > ? , [ ] { } ' " |.
Dates
To make sure your files stay in chronological order, insert dates as YYYYMMDD.
Versioning
Consider using leading zeros (001, 002 … 010 … 100) for version numbers so files sort in numeric order.
Consistency
Finally, keep your file naming as consistent as possible within the same assignment or project.
- SOC320_SMM_20180205_v001
- SOC320_SMM_20180205_v002
- SOC320_SMM_20180205_v010
Rename our sample workbook
- Click
Filethen clickSave As - Browse to find a location to save the workbook
- Rename the file and add:
- Your name or initials
- Today’s date
- A version number
- Click
Save